11 May 2023
Opening up new horizons in Niger in both hydrocarbons and renewable energy
Our assets
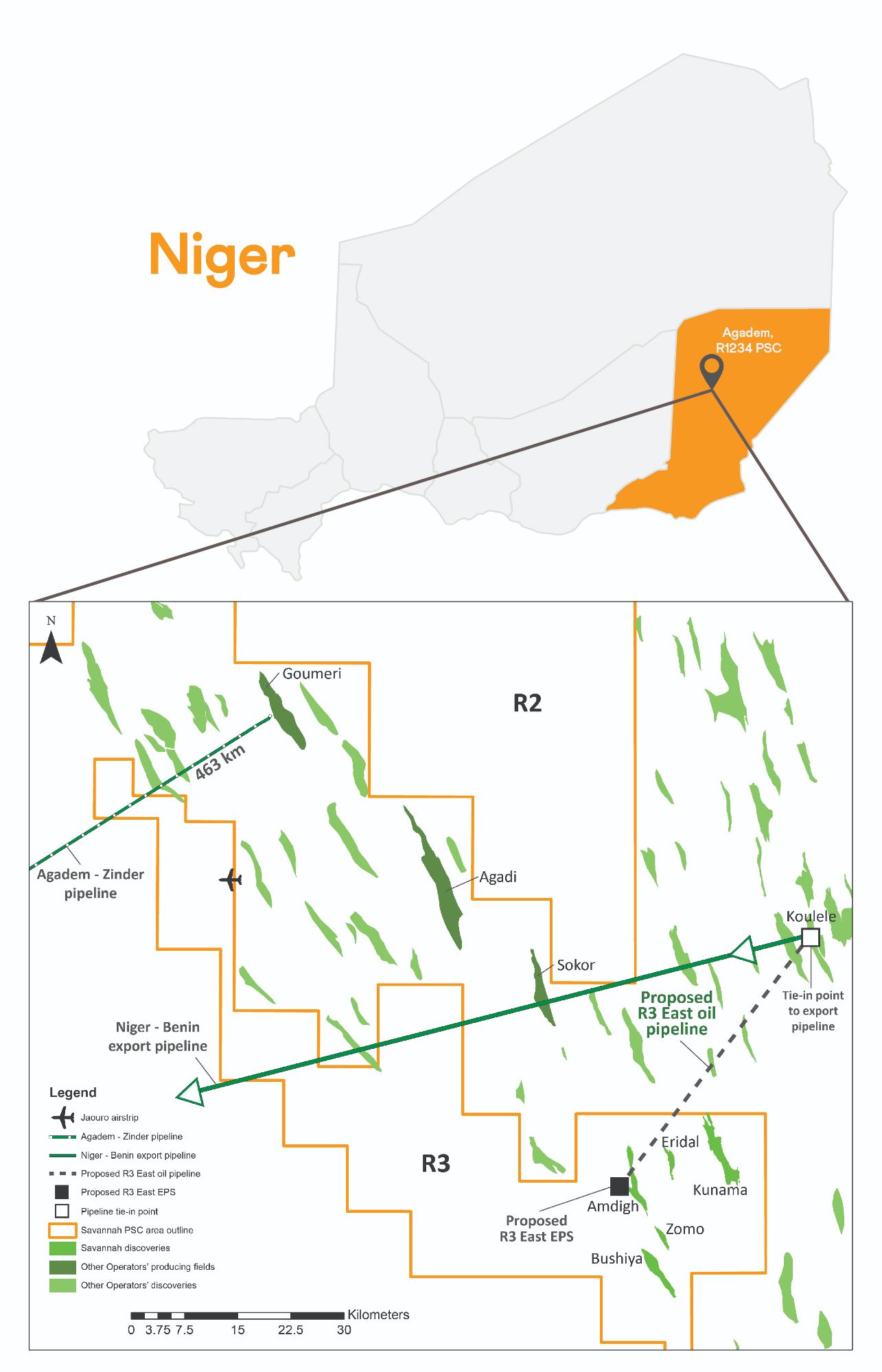
Hydrocarbon licence interests
Savannah's hydrocarbon licence interests via the R1234 Production Sharing Contract ("PSC") cover approximately 13,655 km2, equating to 50% of Niger's main petroleum basin, the Agadem Rift Basin (ARB) in South East Niger.
35 MMstb
Gross 2C Resources for our R3 East discoveries.
90 MMstb
Additional Gross Unrisked Prospective Resources (best case) from five prospects and leads withing tie-in distance to the planned R3 East facilities.
100% exploration success rate
Achieved to date with five discoveries from five wells drilled.
146
Potential exploration targets.

Our progress in the ARB
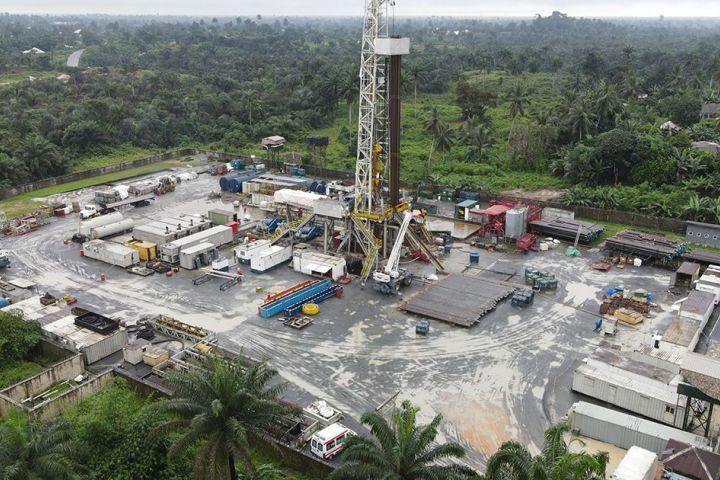
Savannah entered into two onshore Production Sharing Contracts ("PSCs") in Niger in 2014 and 2015 – R1/R2 and R3/R4. During H1 2022, the four licence areas in Niger were amalgamated into a single PSC (R1234). This has laid the foundation to progress plans for the R3 East Early Production Scheme.
Since entering into our two PSCs, we have successfully conducted a series of extensive work programmes in the ARB. This has included the acquisition and interpretation of new airborne geophysical (2014/15) and 3D seismic (2016/17) surveys, the construction of an extensive proprietary basin-wide subsurface model (2014 to date), five discoveries from five wells across five oil fields (2018) and the submission of our initial field development plan to the Nigerien authorities (2019).
There are an additional five prospects and leads within tie-in distance to the planned R3 East facilities with three Yogou Cretaceous prospects mapped on 3D seismic, at depths below our main discoveries (i.e. Amdigh, Eridal and Bushiya), and two leads in the Central part of R3. Savannah has identified 146 potential exploration targets in total across our licence area to consider drilling in the future.
Read more about the geology
of the ARB in our
2022 Annual Report and Accounts

Parc Eoilen de la Tarka
Savannah is developing Niger’s first wind farm, Parc Eolien de la Tarka, to be located in the Tahoua Region of southern Niger. In September 2023, having completed one year of wind measurements from our 100m meteorological mast, we found that wind speeds at Tarka were higher than our initial assessments, resulting in an increase in estimated power production to 800 Gwh per year from 600 GWh per year. Using our recorded data (wind speed, wind direction, temperature, pressure, and humidity), we have worked with wind turbine suppliers to provide an optimised technical solution, utilising fewer wind turbines with a higher capacity than originally envisaged, to meet the same proposed generation capacity of up to 250 MW.
Up to 250 MW
Proposed installed power generation capacity.
35-40 wind turbines
Expected to comprise between 35 to 40 wind turbines.
Up to 800 GWh per year
Expected to produce up to 800 GWh per year of electricity.
22%
Expected to supply up to 22% of Niger’s electricity demand.

Niger solar projects
Savannah is planning to develop two photovoltaic power plants in Niger.
Up to 200 MW
Two solar photovoltaic power plants, of up to 100 MW each, expected to be located within 20km of the cities of Maradi and Zinder, respectively, in southern Niger.
Grid connection
Expected to be connected to the South Central section of Niger’s electricity grid.
Avoiding up to 260 kt of CO2
Expected to avoid up to an estimated 260,000 tonnes of annual CO2 emissions1.
12%
Expected to supply up to 12% of Niger’s electricity demand.
1 Calculation based on European Investment Bank (EIB) Project Carbon Footprint Methodologies, Methodologies for the Assessment of Project GHG Emissions and Emission Variations, July 2020.






















